97 câu Trắc nghiệm Chuyên đề 11 Unit 6. Global warming
36 người thi tuần này 5.0 2.9 K lượt thi 97 câu hỏi 45 phút
🔥 Đề thi HOT:
Bộ 5 đề thi học kì 1 Tiếng Anh 11 Global Success có đáp án (Đề 1)
Đề thi cuối kì 1 Tiếng Anh 11 Friends Global có đáp án- Đề 1
23 câu trắc nghiệm Tiếng Anh 11 Global Success : Từ vựng: ASEAN và các nước thành viên có đáp án
10 câu trắc nghiệm Tiếng Anh 11 Global Success Reading đọc hiểu: Cities of the future có đáp án
23 câu trắc nghiệm Tiếng Anh 11 Global Success Từ vựng: Sức khỏe và thể chất có đáp án
Đề thi giữa kì 1 Tiếng Anh 11 Friends Global có đáp án- Đề 1
Nội dung liên quan:
Danh sách câu hỏi:
Lời giải
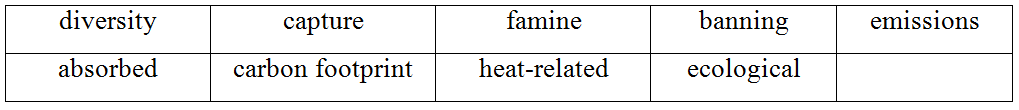
1. Đáp án: d
Giải thích: atmosphere (n.): khí quyển
Dịch nghĩa: the mixture of gases that surrounds the earth (hỗn hợp khí bao quanh trái đất)
2. Đáp án: f
Giải thích: famine (n.): nạn đói
Dịch nghĩa: a lack of food during a long period of time in a region (thiếu lương thực trong một thời gian dài ở một khu vực)
3. Đáp án: b
Giải thích: drought (n.): hạn hán
Dịch nghĩa: a long period of time when there is little or no rain (một khoảng thời gian dài khi có rất ít hoặc không có mưa)
4. Đáp án: e
Giải thích: lawmaker (n.): nhà lập pháp
Dịch nghĩa: a person in government who makes the laws of a country (người trong chính phủ làm luật cho một quốc gia)
5. Đáp án: a
Giải thích: ecosystem (n.): hệ sinh thái
Dịch nghĩa: all the plants and living creatures in a particular area (tất cả các loài thực vật và sinh vật sống trong một khu vực cụ thể)
Câu 2
Lời giải
Đáp án: D. drought
Giải thích:
A. flood (n.): lũ lụt B. wind (n.): gió
C. sunlight (n.): ánh nắng D. drought (n.): hạn hán
Xét về nghĩa, phương án D phù hợp nhất.
Dịch nghĩa: There has been no rain for 3 months in the region. Trees are going to die because of drought. (Không có mưa suốt 3 tháng ở khu vực này. Cây sẽ chết vì hạn hán mất.)
Câu 3
Lời giải
Đáp án: B. banned
Giải thích:
A. allowed (v.): cho phép B. banned (v.): cấm
C. supported (v.): ủng hộ D. encouraged (v.): khuyến khích
Xét về nghĩa, phương án B phù hợp nhất.
Dịch nghĩa: Because CFC may cause ozone depletion, it has been banned globally. (Vì CFC có thể gây ra sự suy giảm tầng ozone nên nó đã bị cấm trên toàn cầu.)
Câu 4
Lời giải
Đáp án: A. greenhouse
Giải thích:
A. greenhouse (n.): nhà kính B. moisturized (adj.): có độ ẩm
C. wet (adj.): ướt át D. natural (adj.): tự nhiên
Xét về nghĩa, phương án A phù hợp nhất.
Dịch nghĩa: Water vapour is surprisingly considered a greenhouse gas as it partially makes the Earth warmer. (Ngạc nhiên thay, hơi nước được coi là một loại khí nhà kính vì nó phần nào làm cho Trái Đất ấm hơn.)Câu 5
Lời giải
Đáp án: D. Climate
Giải thích:
A. Hailstorm (n.): mưa đá B. Heatwave (n.): sóng nhiệt
C. Lightening (n.): sấm sét D. Climate (n.): khí hậu
Xét về nghĩa, phương án D phù hợp nhất.
Dịch nghĩa: Climate change can be in the form of hotter summer, longer drought or more hurricanes. (Biến đổi khí hậu có thể khiến cho mùa hè nóng hơn, hạn hán kéo dài hơn hoặc nhiều bão hơn.)
Câu 6
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 7
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 8
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 9
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 10
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 11
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 73
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 74
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 75
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 76
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 77
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Đoạn văn 1
Read the passage and decide whether the statements are True or False.
When considering the relationship of drought to climate change, it is important to make the distinction between weather and climate. Weather is a description of atmospheric conditions over a short period of time, while climate is how the atmosphere behaves over relatively long periods of time. Individual drought periods can be understood as discrete weather events. Climate changes occur over longer periods and can be observed as changes in the patterns of weather events. For instance, as temperatures have warmed over the past century, the prevalence and duration of drought has increased in the American West. Global climate change affects a variety of factors associated with drought. There is high confidence that increased temperatures will lead to more precipitation falling as rain rather than snow, earlier snowmelt, and increased evaporation and transpiration. Thus the risk of hydrological and agricultural drought increases as temperatures rise. Much of the Mountain West has experienced declines in spring snowpack, especially since mid-century. These declines are related to a reduction in precipitation falling as snow (with more falling as rain), and a shift in timing of snowmelt. Earlier snowmelt, associated with warmer temperatures, can lead to water supply being increasingly out of phase with water demands. While there is some variability in the models for western North America as a whole, climate models unanimously project increased drought in the American Southwest. The Southwest is considered one of the more sensitive regions in the world for increased risk of drought caused by climate change.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Đoạn văn 2
Read the passage and choose the best answer to each of the following questions.
The glaciers of the Himalayas and the Andes could disappear in this century. As a result, the millions of people in India, Bolivia and Peru who now depend on melting water from mountain glaciers could find themselves in a critical situation. The ice sheet of Greenland is also melting more quickly than the scientists predicted. Greenland’s largest outlet glacier, the Jakobshavn Ibra glacier, is moving toward the sea twice as fast as it was in 1995. One cause could be meltwater that runs down to the bottom of the glacier and gets between the ice and the rock below. This water makes it easier for the glacier to slide along to the ocean. Many ice researchers believe that Greenland’s melting, if it continues, will add at least three feet to global sea levels by the year 2100. If the ice sheet of Antarctica, now largely unaffected, begins to melt, the next few conturies could see a six-foot rise in sea levels, forcing tens of millions of people out of their homes. (Reading Explorer 2)
Câu 93
A. to explain the problems of melting glaciers
B. to suggest how to slow the melting of glaciers
C. to illustrate how glaciers were formed and disappeared
D. to explain the causes of global warming
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 94
A. The ice sheet of Antarctica will begin to melt.
B. Tens of millions of people will be forced out of their homes.
C. The melting of Antartican ice will add six feet to sea levels.
D. Global sea levels will rise at least three feet.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 95
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 96
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Câu 97
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.